If you own or manage a retail business, it is useful to know the four social styles. When you understand an individual’s default social styles, you can create more meaningful customer interactions resulting in improved customer experiences. In this post, we’ll outline the four social styles and explain how understanding them can help improve your interactions with customers. We’ll also provide some tips on how to adjust your communication approach depending on the customer’s social style and circumstances.
Note: Companies such as Home Depot have been training their sales staff in Social Styles since the 1990s.
What are the four Social Styles Models?
The four social styles (aka, personality styles or communication styles) are social or personality dispositions designed to help us understand personality characteristics. While the social styles model does not define use in absolute terms, it is useful in that the model recognizes that individuals have a dominant or default personality disposition.
Social Styles in the Business Context
Knowing how to apply social styles helps employees and managers communicate with customers, employees, and other stakeholders more effectively and persuasively. Therein, strong communicators can learn how to take advantage of their default social style to maximize their work productivity. Furthermore, employees who understand social styles can adapt to social situations more effectively ensuring they are communicating in the right style under the right circumstances.
The Benefits of Understanding the four personality styles
When managers and employees understand the 4 social styles, they can learn to identify them in customers, coworkers, and managers. This will allow your staff to communicate more effectively in work and social settings, leading to more productive work and personal relationships.
The Basic Four Quadrant Model Explained
As shown above, the basic four quadrant model helps to organize and map social characteristics along two axes. On the horizontal axes, we can see introverts on the left side and extroverts on right. The vertical axes show thinker on the top and feeler on the bottom.
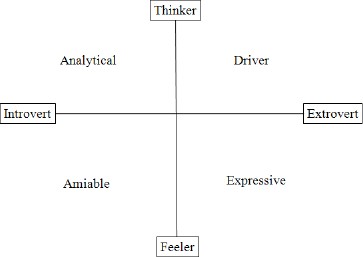
Introverts are typically described as less assertive, quiet, reflective, and taking time to make decisions. On the other hand, extroverts are described as assertive, vocally expressive, and quick to make decisions. Feelers are socially responsive, jovial, and focused on feelings. Whereas thinkers are less responsive to others, serious, reserved and focused on analytics and facts.
Social Style # I: The Driver: Controlling, Decisive & Fast-paced
The driver’s personality falls into the extrovert-thinker; individuals in this sector are generally described as being dominant, independent, candid, decisive, pragmatic, and efficient. The driver personality type emphasizes overcoming barriers and obstacles to achieve results. Drivers are task focused, prefer to command and control, and require challenges to thrive.
Famous examples of the driver personality type include Henry Ford I and Charles Lindbergh.
How to identify an individual with the Driver Social Style:
- Know what they want
- Have little difficulty conveying their conclusions about anything that concerns them
- Focus on the immediate time frame versus the past or future
- Show limited concern for people’s feelings or relationship dynamics
- Come off as harsh, severe, or critical due to their limited attention to relationships
- Seek to command or control situations
- Use and manage time in a disciplined manner
A driver’s strengths include persistence, determination, competitiveness, decisiveness, and optimism. In contrast, a driver can come off as controlling, insensitive, inconsiderate, hostile, judging, and unforgiving.
Strategies for approaching people with the driver’s social style:
-
- Respect their time
- Stick to facts
- Follow up on promises
- Show your competence
- Earn their trust
- Allow them to lead the conversation (listen more, speak less)
Social Style # II: The Expressive Style: Enthusiastic & Emotional
The expressive personality falls in the extrovert-feeler quadrant. Individuals in this sector are generally described as being charming, enthusiastic, persuasive, charismatic, and spontaneous. This personality type emphasizes influencing or persuading others through personality, charisma, and words. Expressive personalities tend to be people focused; often seeking popularity, recognition, and attention.
Famous examples of the expressive personality type from history include Winston Churchill and Franklin Roosevelt.
How to identify individuals with expressive style personality characteristics:
- Focus their attention on the future with intuitive visions and outspoken spontaneity
- Make decisions quickly, based on feelings and opinions
- Come off as warm and approachable, yet competitive for recognition and involvement in relationships
- Behave in stimulating, exciting, impractical, and overly emotional ways
- Tendency to act on opinions, hunches, and intuitions, rather than facts and data
- Generate enthusiasm and optimism through speeches and conversation
- Use time in an undisciplined manner
Expressive social strengths include compassion, the warmth of personality, and generosity. Social weaknesses could include undisciplined, disorganized, unproductive, dramatic, hasty, and manipulative.
Strategies for approaching people with the expressive social style:
-
- Laugh with them
- Listen to their opinions
- Think big picture
- Recognize their contributions
- Lighten the conversation
- Form a relationship vs. a transactional
Social Style # III: The Amiable Style: Friendly, Supportive & Relationship-driven
The amiable personality falls in the quadrant formed by the boundaries of Introvert/Feeler. Individuals in this quadrant are generally described as being steadfast, cooperative, supportive, diplomatic, patient, and loyal. This personality type emphasizes cooperating with others to carry out a task. Amiable personalities tend to focus on people, seek sincere appreciation, and need time.
Famous examples of the Amiable personality type include Robert E. Lee and Dwight D. Eisenhower.
People are seen as having an Amiable Style and appear to:
- Focus on the present and interpret their social environment based on feelings and relationships with people
- Have difficulty understanding that some people react to the information available, or the practicality of the situation, rather than relationships
- Develops effective social networks, work well in teams and supporting roles
- Communicates effectively and shares information openly with colleagues
- Prefers to remain in their comfort zone, avoid risks and interpersonal conflict
- Avoid decisions that might involve personal risks and conflict in relationships
- Tendency to manage time poorly
Strengths; amiable individuals tend to be organized, easy-going, empathetic, dependable, and practical. Their weaknesses include stubbornness, unmotivated, self-protective, needy, and dependent.
Strategies for approaching people with the amiable social style
-
- Approach conflict carefully
- Get to know them and let them get to know you
- Consider their perspectives
- Apply tact to draw out their opinions
- Provide feedback and handle issues in private
- Listen carefully and be courteous
Social Style # VI: The Analytical Style: Thoughtful, Reserved & Slow-paced
The analytical personality style falls in the introvert-thinker quadrant. Individuals in this sector are generally described as being logical, thorough, systematic, prudent, cautious, and rules-based. Analytic individuals emphasize working conscientiously to ensure quality and accuracy. Analytical personalities tend to focus on tasks, seek details and facts, and need structure to thrive.
Famous examples of the Analytical personality type include Thomas Jefferson and Albert Einstein.
People are seen as having an Analytical Style appear to:
- Communicates using facts, data, metrics, proven examples and logic
- Excellent at problem-solving, planning, and organizing people, work, and organizations
- May appear to lack enthusiasm, seem cold and calculating or detached
- live their lives according to a set of ideals, codes, and principles
- Focus on processes, procedures, rules, and systems.
- Manage and use time well
Analytics are often perfectionists, idealistic, sensitive, self-disciplined, and precise. Weaknesses include moodiness, negative, critical, rigid, legalistic, unsociable, and impractical.
Strategies for Working with The Analytical Style Person
-
- Take your time with them
- Communicate clearly and concisely
- Refrain from placing pressure to answers
- Respect their reasoning process
- Pose direct questions and give direct feedback
- Give them space and respect personal boundaries
Applying the knowledge of social styles can help create more meaningful customer interactions, improving the overall customer experience. By understanding an individual’s default social style and adjusting your communication approach accordingly, you can connect with customers in a way that feels natural and comfortable for them. Have you tried using social styles to improve your customer interactions? Let us know how it went in the comments below!
Thank you for reading our article!
TimeWellScheduled.com is a secure, online time and attendance software that is 100% tailored to meet your scheduling needs! In addition, TimeWellScheduled facilitates employee attendance tracking and payroll tasks and enhances your staff management capabilities. Plus, our service is free for up to 10 employees!
Click: here to download our (Excel) employee scheduling template; It’s FREE!





