“Retail environments have become places where consumers look for unique and memorable experiences, not just products. Compared to traditional retail environments, space becomes “alive” and gives customers the opportunity to interact actively with the brand, and on all levels.” – Ghalia Boustani, Retail Consultant.
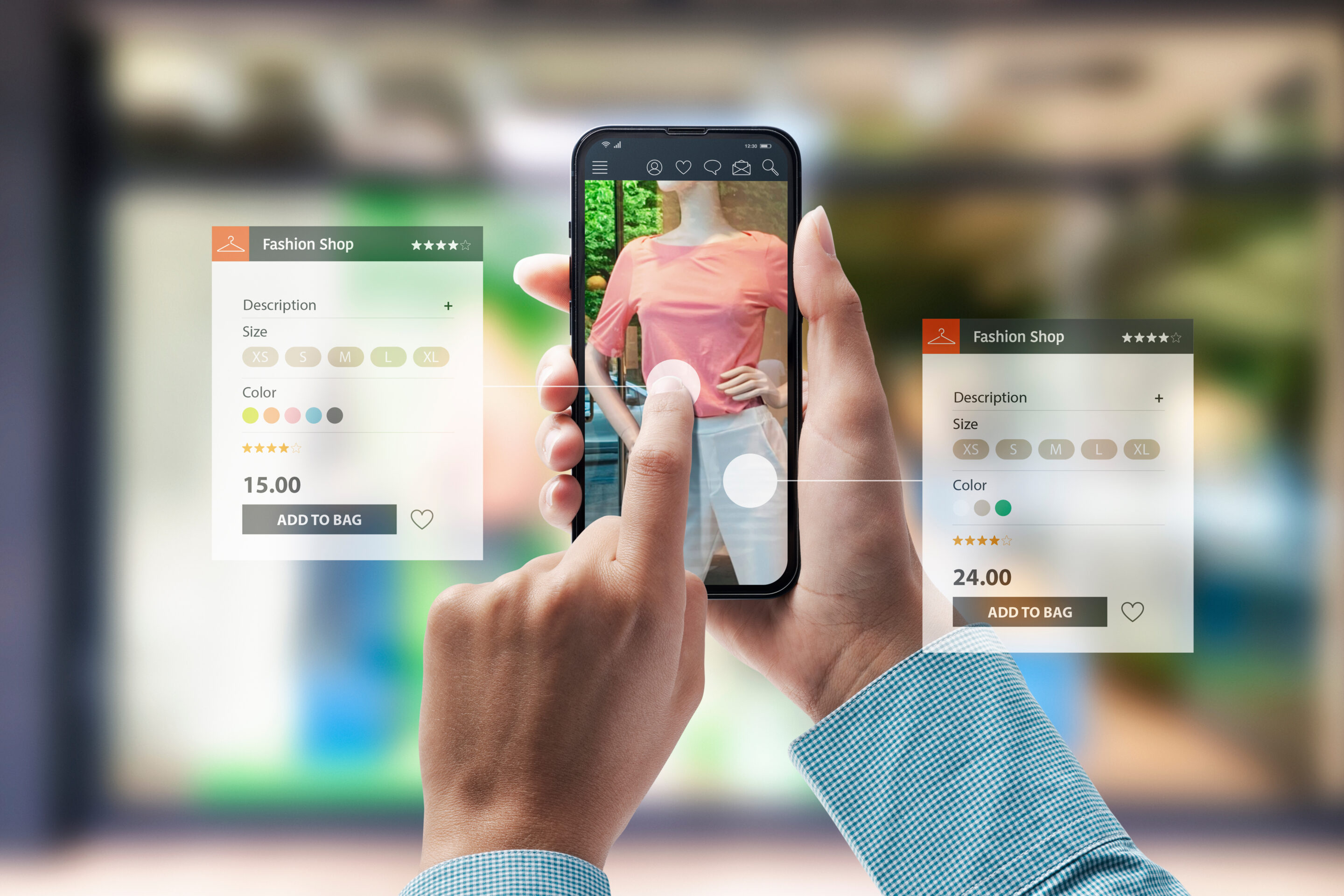
Immersive retail reshapes how consumers shop by merging digital technology with sensory engagement. As customers increasingly demand interactive experiences, retailers leverage this innovative approach to enhance shopping experiences and optimize operations.
Even so, the journey comes with challenges, from the cost and complexity of implementing immersive technologies to the need for consumer education and compelling content creation.
This article discusses these challenges, shedding light on how retailers can navigate the obstacles to successfully integrate immersive retail solutions.
How Does Immersive Retail Work?
Immersive retail is the application of multi-sensory experiences enabled via a combination of interactions that create highly memorable and emotional value for shoppers. These interactions can be presented in different ways:
- Flat interfaces, for example, with the use of interactive touch screens.
- Natural interfaces like voice, spatial, gesture-based, auditory, or olfactory.
- Extended reality, such as 3D, augmented, virtual, or mixed.
Immersive experiences provide retailers with several benefits versus traditional retail environments. Moreover, they have the impact of accelerating purchasing decisions, improving conversion rates, reducing the number of returns, and increasing customer loyalty.
Why Is Immersive Retail A Trend?
Immersive retail has surged as a prominent trend due to its ability to meet evolving consumer demands and preferences. The shift towards e-commerce, accentuated by the pandemic, prompted retailers to seek innovative ways to enhance the user experience.
Technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) offer unique opportunities for consumers to interact with products in immersive digital environments, bridging the gap between online and in-store shopping.
What Are Immersive Technologies
Immersive technologies attempt to emulate the physical world through a digital or simulated one, creating the sensation of immersion.
The aim is to modify sensory perception, offering personalized experiences that break the barriers of space and time. Technologies such as augmented, virtual, and mixed reality are combined to achieve this.

Source: Forbes Technology Council
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR overlays digital information or virtual objects onto the real world, typically viewed through smartphones or AR glasses. It enhances real-life experiences by adding computer-generated elements, such as 3D graphics or information, to a user’s surroundings.
Virtual Reality (VR)
VR immerses users in entirely computer-generated environments, cutting them off from the real world. VR headsets create a simulated reality where users can interact with a wholly digital environment, making it ideal for applications like gaming, training simulations, and immersive experiences.
Mixed Reality (MR)
MR blends aspects of both AR and VR, enabling users to interact with virtual objects while remaining aware of their real-world surroundings. MR headsets, like Microsoft HoloLens, seamlessly integrate virtual and physical elements, making them suitable for tasks requiring interaction with digital and physical environments, such as design and engineering.
“Consumers are becoming pickier about the brands and stores they choose. This means they’re looking for unique and flawless shopping experiences. It also means it’s harder to grab and keep their attention.” – 4Experience Crew.
What Benefits Does Immersive Retail Offer?
The following examples illustrate how immersive retail creates engaging experiences, enhances product visualization, improves employee training, optimizes space, and contributes to sustainability efforts.
1) Enhanced Customer Engagement
- Immersive retail experiences make customers more emotionally connected to brands and products.
- Many retailers embrace immersive technologies like AR and VR to create interactive experiences that captivate customers.
Example: Nike has implemented “Nike Fit AR,” where customers can use their smartphones to scan their feet. This engagement tool helps customers find the perfect-fitting shoes, strengthening their bond with the Nike brand.
2) Improved Product Visualization
- Immersive technologies, including AR and VR, empower customers to visualize products more comprehensively, assisting them in making well-informed purchasing decisions.
- Retailers increasingly utilize these technologies to enhance how customers perceive and interact with their products.
Example: IKEA’s AR application tool enables customers to place furniture items virtually in their homes before purchasing. It’s a prime example of how immersive technology improves product visualization and assists customers in understanding how items will fit into their living spaces.
3) Streamlined Employee Training
- Immersive technology, particularly Virtual Reality, offers an efficient training method for retail employees, especially for high-pressure scenarios.
- Retailers are adopting VR-based training programs to equip their staff with the skills to handle demanding situations effectively.
For example, Walmart utilizes VR for employee training. The company has developed a VR-based training program to prepare its associates for intense events like Black Friday. This ensures that employees are well-prepared to manage large crowds and provide a smooth shopping experience for customers.
4) Space Optimization
- Mixed Reality technology optimizes inventory space, allowing retailers to offer a wide range of products without overcrowding physical stores.
- MR technology blends the physical and digital worlds, providing customers access to a vast product selection in a compact physical space.
Example: Sephora, a popular cosmetics retailer, employs AR mirrors in its stores. These mirrors enable customers to virtually try on makeup products without using physical samples. This saves space and offers a broader range of choices for customers.
5) Sustainable Merchandising
- Immersive retail supports sustainable merchandising by replacing traditional manual processes with digital alternatives.
- Retailers are increasingly focused on sustainability, and immersive technologies are aiding this endeavor by reducing the need for printed materials and physical samples.
Example: Similar to Nike, Adidas introduced its AR app, allowing customers to scan their sneakers. This app grants access to exclusive digital content related to the product. In doing so, Adidas reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional printed materials, such as product tags and brochures.
“56% of consumers said more stores should offer immersive shopping” – (Source: Acxiom)
Challenges in Implementing Immersive Retail
While the potential rewards of immersive retail are significant, challenges can arise during implementation. Technological hurdles, staff adaptation, and consistency are some obstacles businesses may face. Consider the following challenges:
1) Cost and Investment
Immersive retail technologies, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), come with a significant financial burden. Retailers face the challenge of allocating substantial budgets for hardware, software development, content creation, and ongoing maintenance. This financial commitment can strain resources and budgets for many businesses, especially smaller ones.
To successfully implement immersive experiences, retailers must carefully consider the costs and weigh them against the potential benefits. Finding cost-effective solutions and exploring partnerships or financing options can help alleviate this challenge.
2) Technical Complexity
The technical intricacies of immersive technologies can be intimidating for retailers. Integrating AR, VR, or MR into existing systems and processes demands a deep understanding of these technologies. Ensuring seamless connectivity, high-performance hardware, and robust software development can be daunting.
Retailers may need to invest in specialized expertise or collaborate with technology partners to navigate these complexities effectively. Technical training and ongoing support are essential to ensure the smooth operation of immersive solutions.
3) Consumer Adoption
Convincing consumers to embrace immersive retail experiences can take time and effort. Not all shoppers are familiar with or comfortable using AR, VR, or MR. This challenge requires retailers to invest in education and marketing efforts.
Communicating the benefits of immersive experiences, such as enhanced product visualization or interactive try-ons, is crucial. Retailers must create awareness and build trust to encourage customers to engage with these technologies. Providing user-friendly interfaces and clear instructions can help ease the adoption process.
4) Content Creation
Crafting compelling and relevant content for immersive experiences is a substantial challenge for retailers. Creating engaging assets requires creativity, time, and resources, whether it’s developing virtual try-on experiences, AR product visualizations, or VR simulations.
Retailers must invest in content creation teams or collaborate with content creators who understand the unique demands of immersive technologies. Regularly updating and refreshing content to keep it appealing and relevant is essential to maintain consumer interest.
5) Scalability and Integration
Scaling immersive retail solutions across multiple stores or locations while ensuring seamless integration with existing operations can pose difficulties. Maintaining consistency in the quality of immersive experiences and compatibility with the broader retail ecosystem is essential.
Retailers need to develop a clear strategy for scaling their immersive offerings, taking into account factors like hardware deployment, software updates, and content distribution. Effective project management and ongoing monitoring can help overcome scalability and integration challenges.
“Physical distribution environments are no longer regarded as mere sources of supply. As customers can access the product from the comfort of their homes, they view retail formats differently. Their visit to the store should present them with opportunities not found online, or that go beyond the traditional features of the store.” – Ghalia Boustani, Retail Consultant.
Conclusion
The journey towards immersive retail holds numerous challenges, but the potential rewards are equally compelling. Embracing immersive technologies allows businesses to meet the growing consumer demand for engaging experiences and unlocks new avenues for growth and differentiation. Thus, the future of retail lies in the effective integration of immersive retail experiences, blending the physical and digital worlds to create unique and memorable customer journeys.
Thank you for reading our article!
TimeWellScheduled is a secure online time and attendance software that is 100% tailored to meet your scheduling needs! In addition, our cloud-based scheduling solution optimizes employee attendance tracking, simplifies payroll administration, and enhances staff management capabilities. Plus, our service is free for up to 10 employees!
Click here to download our (Excel) employee scheduling template; It’s FREE!